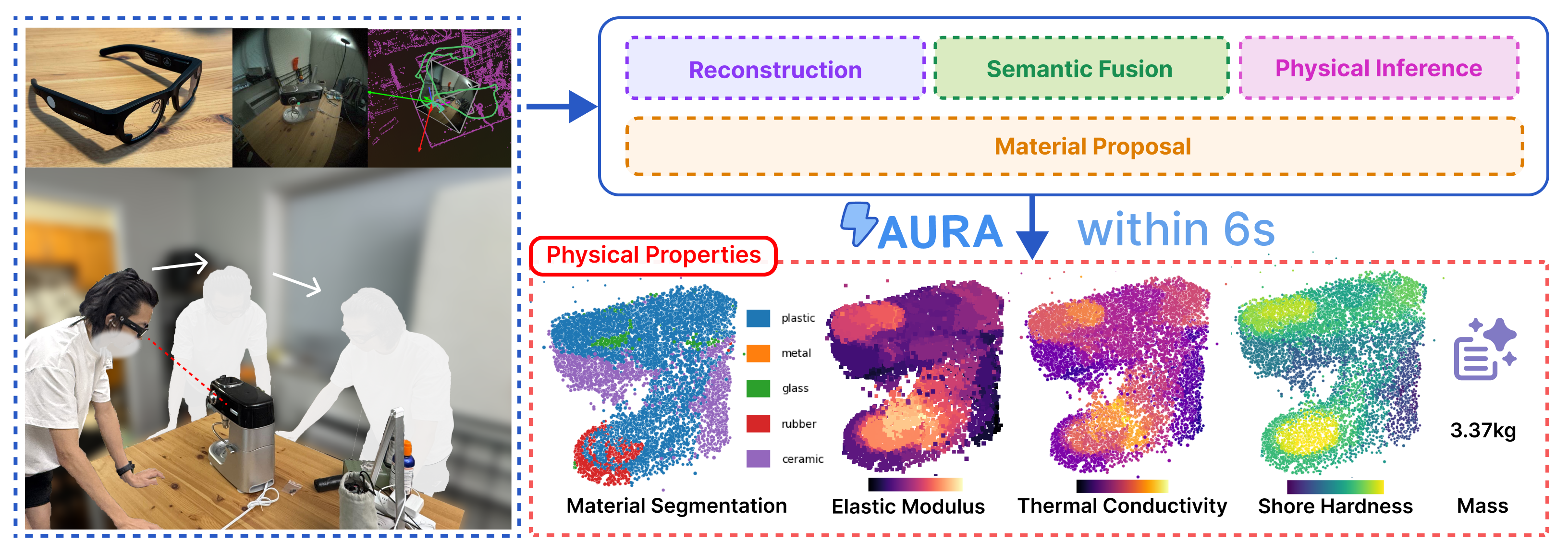

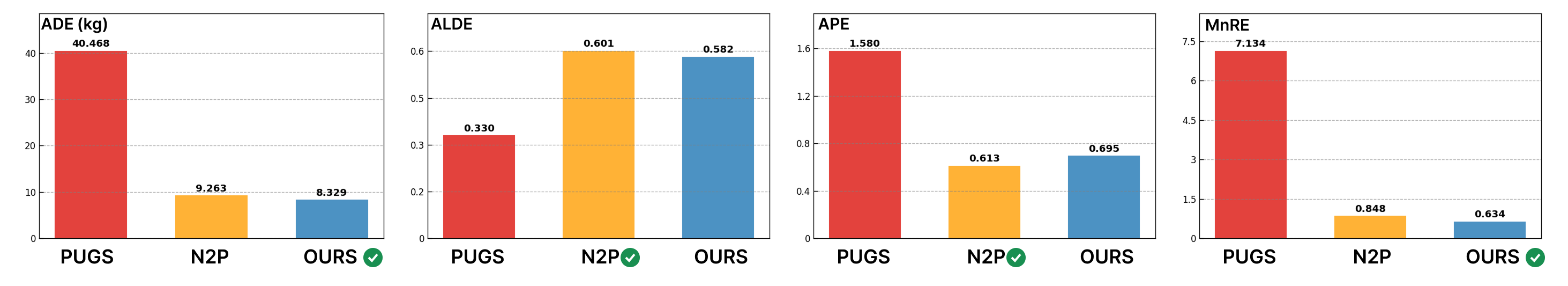
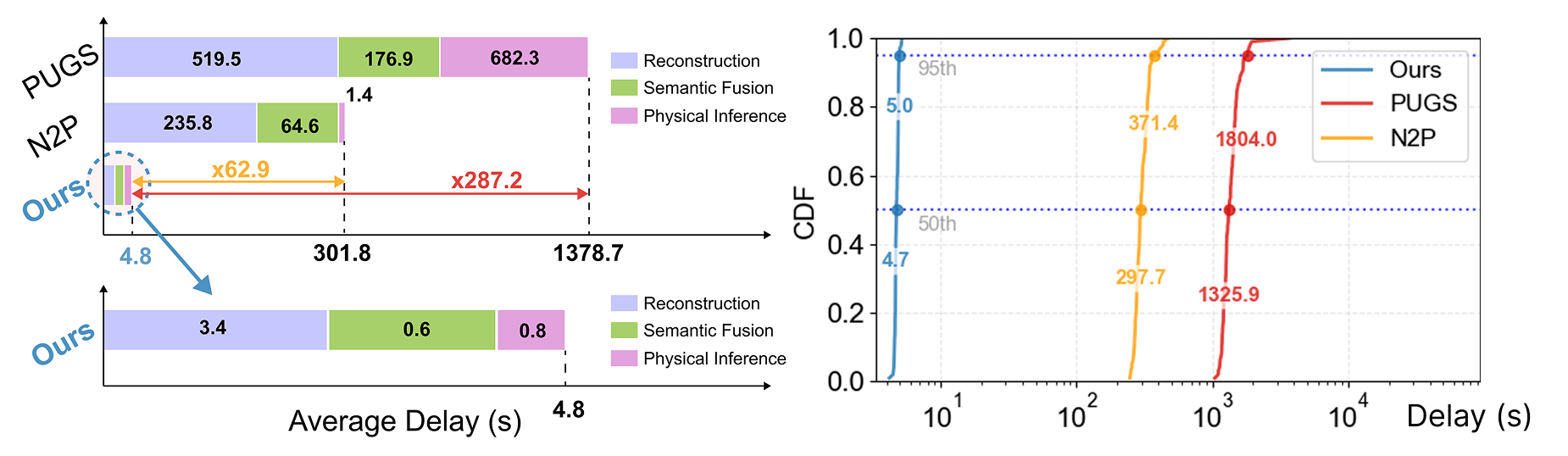
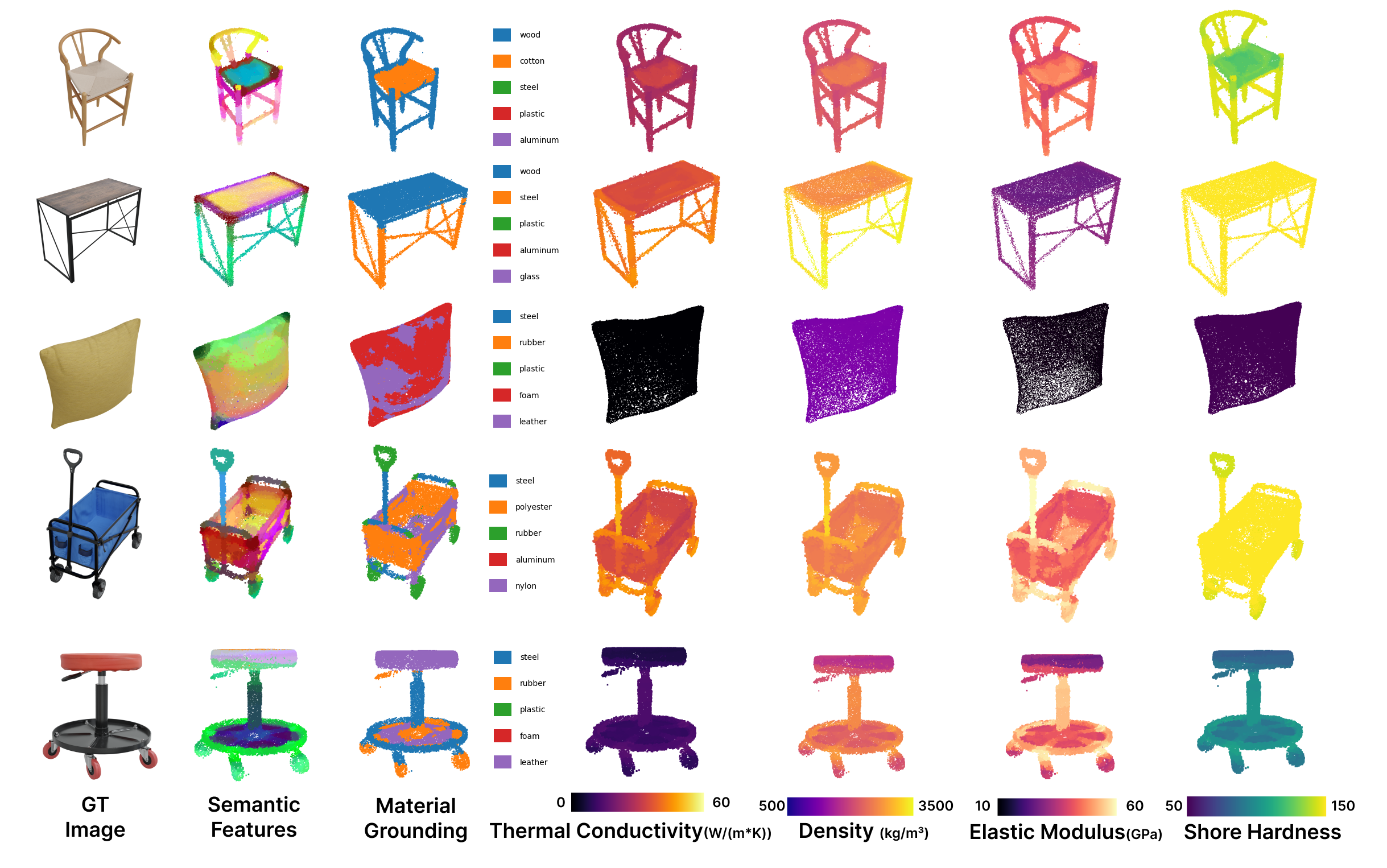
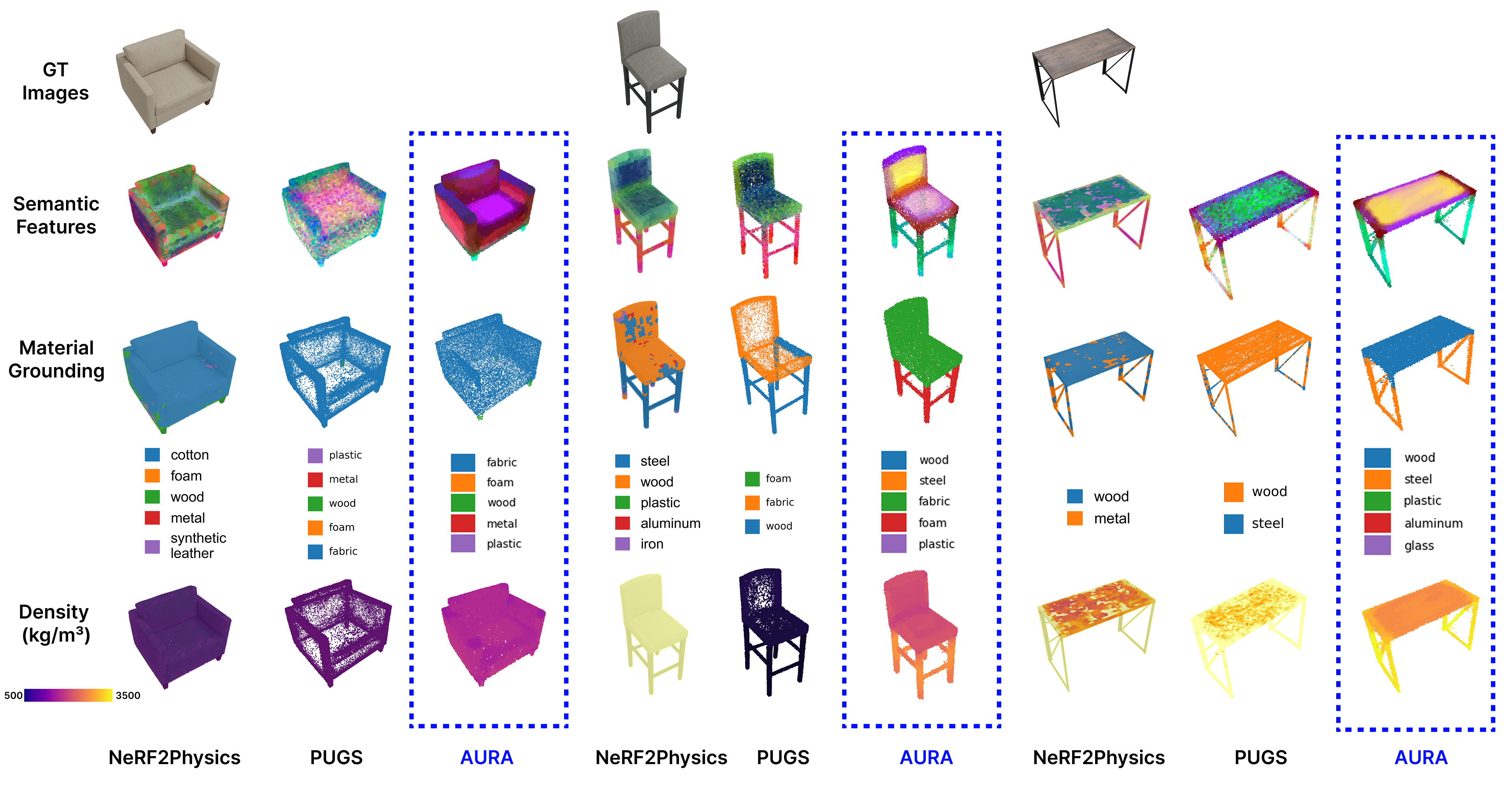
We introduce AURA (Accelerated Understanding and Reasoning Analyzer), a system that accelerates vision-guided physical property reasoning to enable augmented visual cognition. AURA minimizes the run-time latency of this reasoning pipeline through a combination of both algorithmic and systematic optimizations, including rapid geometric 3D reconstruction, efficient semantic feature fusion, and parallel view encoding. Through these simple yet effective optimizations, AURA reduces the end-to-end latency of this reasoning pipeline from 10-20 minutes to less than 6 seconds. A head-to-head comparison on the ABO dataset shows that AURA achieves this 62.9-287.2 times speedup while not only reaching on-par (and sometimes slightly better) object-level physical property estimation accuracy (e.g. mass), but also demonstrating superior performance in material segmentation and voxel-level inference than two SOTA baselines. We further combine gaze-tracking with AURA to localize the object of interest in cluttered, real-world environments, streamlining the physical property reasoning on smart glasses. The case study with Meta Aria Glasses conducted at an IKEA furniture store demonstrates that AURA achieves consistently high performance compared to controlled captures, providing robust property estimations even with fewer views in real-world scenarios.
You are an expert in material analysis and structural estimation. Analyze images from different views of the object to identify materials, estimate thickness, and predict physical properties.
Analysis Steps:
1. Object Assessment: Identify object type and name, categorize as small(<30cm)/medium(30cm-1m)/large(>1m)
2. Structure Analysis: Examine edges, joints, construction method to identify plate-like or tube-like components and its material.
3. Material Selection: Choose top-5 materials that are most likely for this object, making them diverse from each other.
Thickness Estimation Rules:
- Plate-like or tube-like materials: Estimate thickness then DIVIDE BY 2 (due to point cloud integration from all faces)
- Bulk/solid materials: Use normal thickness estimation
- Normal thickness reference: Small objects: 0.05-1cm | Medium: 0.1-1.5cm | Large: 0.5-2.5cm
- Provide narrow ranges (±10% variation)
Physical Properties Guidelines:
- Shore Hardness: A (soft materials 0-100), D (hard materials 0-100)
- Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K): Metals 10-400, Glass/Ceramics 1-10, Plastics 0.1-1, Wood 0.05-0.5, Rubber/Foam 0.02-0.3
- Elastic Modulus (GPa): Metals 20-400, Glass/Ceramics 50-400, Plastics 0.1-10, Wood 5-20, Rubber/Foam 0.001-1
Output Format: You must provide your answer in the following JSON format:
{
"description": "Brief description with size estimate",
"object_category": "small/medium/large",
"estimated_dimensions": "H x W x D in cm",
"materials_and_thickness": [
{
"material": "single_word_name",
"mass_density_kg_m3": "low-high",
"thickness_cm": "low-high",
"shore_type": "A/D",
"shore_hardness": "low-high",
"thermal_conductivity": "low-high",
"elastic_modulus": "low-high"
}
// Exactly 5 materials from different categories
]
}
Critical Requirements:
- Must output exactly 5 materials from 5 different categories
- Material names must be single common words
- For plate-like or tube-like materials, divide estimated thickness by 2
- All materials must be realistic for the analyzed object
BibTex To be Added